How Your Brain Creates Reality: The Science Behind Hypnosis and Neural Shortcuts
Understanding Optical Illusions, the Autokinetic Effect, and Lasting Change
Key Takeaway: Your brain constantly creates your perception of reality by filling in gaps and making educated guesses. This same creative capacity that produces optical illusions can be guided through hypnosis and nervous system regulation to break unwanted patterns and create lasting change.
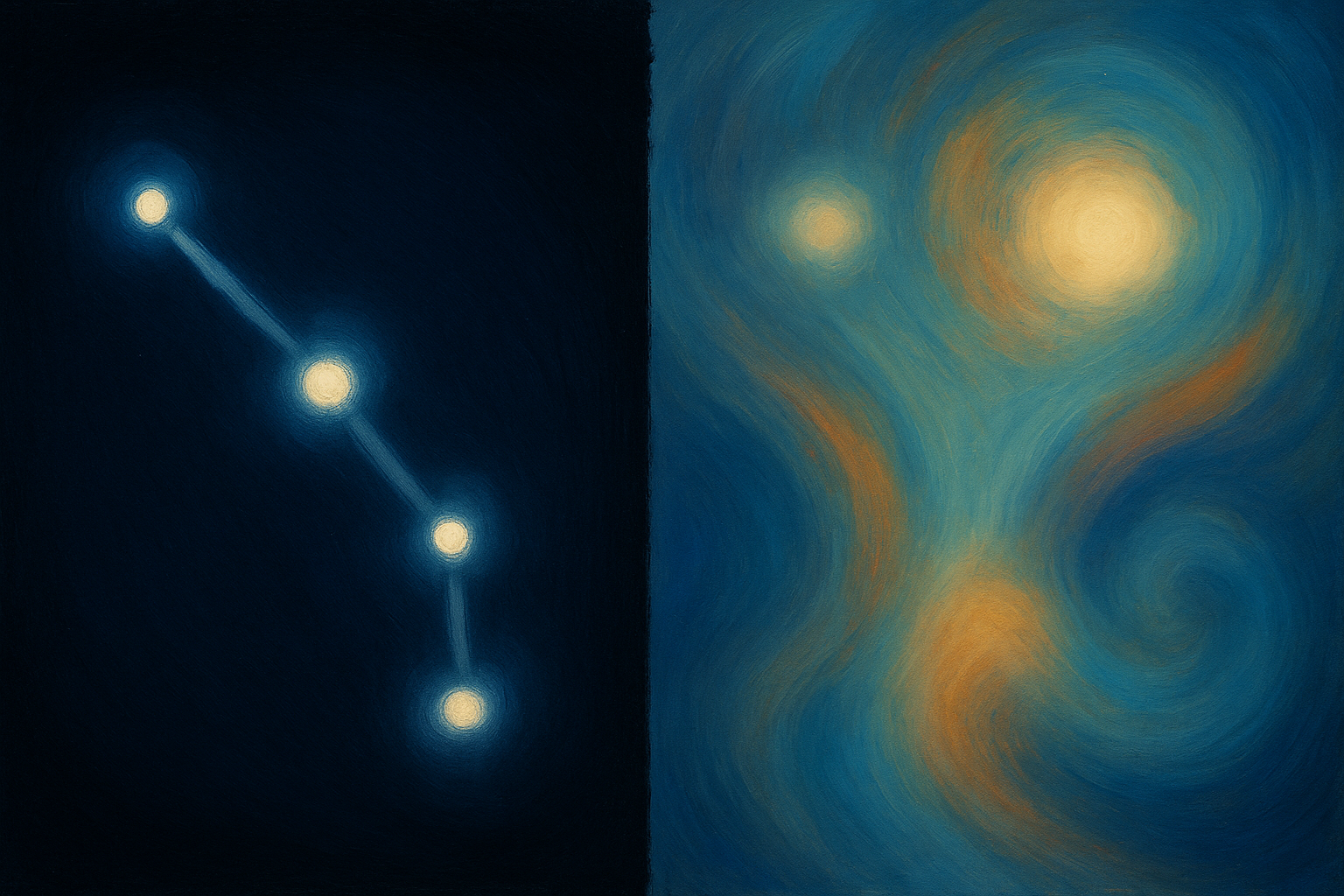
A few nights ago at home on Toad Mountain, I stood looking across the dark valley toward Vancouver, sixty miles away. During the day, it's easy to see that I'm 1000 feet high above the world, where the trees slope downhill, fog pools in the lowlands, and the sea stretches beyond.
At night, everything changes. The horizon rises, and a line of distant lights forms what looks like another hill across from me. The city glows on the hillside, and the valley between us feels close enough to touch.
Then something more strange happens. When I soften my gaze and look slightly away, letting the scene slip into peripheral vision, the lights begin to move or drift, almost imperceptibly, as though I'm standing on the deck of a slow ferry gliding through fog toward shore.
The lights aren't actually moving, of course. But my brain is.
What Is the Autokinetic Effect? Understanding How Your Brain Creates Motion
This is the autokinetic effect - a well-documented optical illusion where stationary points of light in darkness appear to drift and move. Your eyes are always moving, even when you think they're still. In full light, your brain compensates for those micro-movements and anchors the world in place. But in darkness, without landmarks or edges to lock onto, it guesses - and that guess becomes your experience.
Your brain does this constantly, by design. This is not a functional flaw. It fills in what it doesn't know, and invents continuity from the sensory fragments.
This is how you perceive motion in movies. Still images are played fast enough that the brain fills in the (literal) blanks. This is also how you remember the past and imagine the future, and it's how, in hypnosis, you can transform an internal story simply by changing the frame your mind looks through.
Your brain lies to you all the time, but they're creative lies (and actually lies that can heal once you know how to guide them).
How Does Peripheral Vision Affect Your Nervous System?
When I stared directly at the lights, they stopped moving. My foveal vision locked them in place. But the moment I softened my gaze and allowed the scene into my periphery, they began to drift again.
That simple shift from foveal to peripheral vision is the same neurological gateway that The Alpha Sequence trains you to enter.
So what's the difference between foveal and peripheral vision? Foveal attention belongs to the thinking mind - analytical, effortful, narrow. Peripheral awareness belongs to the intuitive mind - fluid, embodied, spacious.
Research confirms this distinction at the level of the nervous system, where foveal vision is linked to sympathetic nervous system activation (the stress response), while peripheral vision engages the parasympathetic nervous system (rest and relaxation).1 When you soften your focus and shift to peripheral awareness, you create the conditions for your nervous system to shift from beta brainwave states toward alpha brainwave states, which is associated with flow, creativity, and deep presence.2
That's why hypnotic induction often begins with "softening the gaze" or "letting your eyes rest." This is intentional, not to lull you into trance, but to free your mind from the illusion of control, where your brain stop gripping and starts perceiving as a unified field.
What Creates Addiction in the Brain? The PVT Shortcut Explained
The brain doesn't just lie about what you see. It also lies about what will make you feel better.
Recent neuroscience research has identified a specific brain region - the paraventricular nucleus of the thalamus (PVT) - that creates learned shortcuts to relief. In groundbreaking studies published in 2024-2025, researchers discovered that the PVT becomes hyperactive when animals learn to associate environmental cues with substances that ease withdrawal symptoms.3,4 The brain essentially creates a fast-pass lane, firing the message: "This makes you feel better."
The first few times that message fired, it was true. That drink, that extra slice of pizza, or that scroll through your phone at 2 AM genuinely did provide some level of relief from suffering - before the hangover, the weight gain, or the shame spiral that came later.
But the shortcut stays installed long after it stops working. This is part of why the addiction persists. The brain keeps firing the same message - "This will help" - even though it's no longer accurate.
It's not being cruel or trying to sabotage you. It's just doing what it was built to do, which is repeat what worked once, even when the data is old. Like those drifting lights on Toad Mountain, your brain is filling in the story based on information that's no longer current. Like those drifting lights on Toad Mountain, your brain is filling in the story based on old data.
As researchers at Scripps Research note: "Addiction often isn't about chasing pleasure - it's about escaping pain."3 The brain isn't biologically built to upgrade itself without conscious intervention. That's actually beautiful when you think about it, because it means we have the capacity to make changes with our conscious mind.
How to Recognize When Your Brain Is Lying to You
I work with people who've promised themselves "just one" a thousand times, and the pattern is always remarkably similar.
So I ask them, very gently: How many times have you told yourself you'll only have one?
"Nearly every time."
And how many times has that been factually true?
"Never." Or maybe, "Once. Years ago."
So we agree the brain is making a promise it never keeps?
They nod.
What would you do if a friend broke the same promise every single day?
That's when something shifts. Not shame. Recognition.
The compassionate approach to changing habits is acknowledging that the brain isn't the enemy here. It's more like a two-year-old who needs love and redirection, who doesn't know any better and is just running old code, maintaining what amounts to a perpetual lie to make you think this thing gives you relief when it actually doesn't anymore.
Your job is to catch the lie in real time, and when you do, you don't scold. You speak the truth, kindly: "No, that's not actually true, is it?"
This has to be done with tremendous love. The brain needs to hear the truth, but it also needs to know you're on the same team, that you're helping it see what's real.
What Is The Alpha Sequence? A Science-Based Approach to Nervous System Regulation
This is where The Alpha Sequence comes in.
You can't catch the lie while you're locked in foveal, analytical thinking. That's the mind that believes the shortcut, that grips harder, trying to control with willpower alone.
But when you drop into an alpha bainwave state - through softening your gaze, allowing your jaw to relax, liberating your tongue from the urge to speak - you access peripheral awareness. This state of mind that can see the pattern rather than being caught inside it.
What happens during The Alpha Sequence:
- External stimuli diminish naturally.
- Your jaw softens and releases tension, which calms the trigeminal nerve and supports healthy vagal tone5 - sending messages to every muscle, nerve, and cell in your body that now is the time to relax.
- Your breathing slows into a comfortable rhythm with a long exhalation, which increases parasympathetic tone and activates the vagus nerve.6
- The prefrontal cortex stops gripping.
- The brain becomes teachable again.
This is where you install the filter, where you practice catching the lie and speaking the truth. The shortcut loses its power because you're no longer taking the exit, no longer following the old map.
You find yourself in exactly the right place, at exactly the right time. Your mind is freed to experience new thoughts, expansive thoughts - or perhaps no thoughts at all. Pure silence, peace, tranquility.
How to Activate the Autokinetic Effect and Drop Into Alpha
Practice Exercise #1: Experiencing the Autokinetic Effect
Next time you're outside after dark, try this simple experiment.
Find a distant light and stare directly at it. Notice that it's still, fixed in place.
Now soften your gaze and let your eyes relax. Look slightly away from the light, keeping it in your peripheral vision rather than your direct focus.
Watch what happens.
The light might drift or seem to move. Your perception might shift in subtle ways. That's your brain doing what it always does - creating experience from fragments of sensory information.
Practice Exercise #2: Catching the Neural Shortcut
Next time the shortcut fires - "This will make you feel better" - try this approach.
Soften your gaze and let your vision go peripheral, like watching those lights drift on Toad Mountain.
Drop into alpha by letting your jaw soften and release. Let your tongue rest without effort. Breathe slowly with a long, comfortable exhale.
Ask the question with genuine curiosity: "Is that actually true?"
Speak the truth to your brain, kindly: "No, that's not what happens. That's the old shortcut talking. But I see you, brain. You're just trying to help . What's actually true is..."
Frequently Asked Questions About the Brain, Hypnosis, and Neural Shortcuts
Can you really change your brain through hypnosis?
Yes. Hypnosis works by accessing the same neuroplasticity mechanisms your brain uses constantly. When you shift into peripheral awareness and alpha brainwave states, the brain becomes more receptive to new patterns and less attached to old shortcuts.
How long does it take to break a neural shortcut?
It varies by individual and pattern, but with consistent practice of techniques like The Alpha Sequence (5-10 minutes daily), most people notice shifts within 2-4 weeks. The key is catching the lie in real time and compassionately redirecting to something else. That something else can become what I love to call "The Adventure of a Lifetime."
Is the autokinetic effect the same as hypnosis?
Not exactly. The autokinetic effect demonstrates how your brain creates perception, which is the same principle underlying hypnosis. Both show that your experience of reality is constructed by your brain—and therefore can be reconstructed.
What is the difference between alpha and beta brainwaves?
Beta brainwaves (13-30 Hz) are associated with active thinking, problem-solving, and stress. Alpha brainwaves (8-13 Hz) are associated with relaxed alertness, creativity, and receptive states. The Alpha Sequence helps you shift from beta to alpha on demand.
Does peripheral vision really activate the parasympathetic nervous system?
Yes. Research shows that peripheral vision is linked to parasympathetic (rest and digest) activation, while focused foveal vision is linked to sympathetic (stress) activation. This is why softening your gaze is such a powerful relaxation technique.
What is the PVT and why does it matter for addiction?
The paraventricular nucleus of the thalamus (PVT) is a brain region that creates learned associations between environmental cues and relief from negative states. In addiction, the PVT fires the message "this will help" even when the behavior no longer provides actual relief.
Can I practice The Alpha Sequence on my own?
Yes. The basic elements - softening your gaze, relaxing your jaw, extending your exhale - can be practiced anytime. For the complete technique and guided practice, visit The Alpha Sequence training.
Key Takeaways: How to Use Your Brain's Creative Capacity for Change
✓ Your brain constantly lies to create your experience of reality - this is a feature, not a bug.
✓ The autokinetic effect demonstrates how perception is constructed, not received.
✓ Neural shortcuts (like the PVT pathway) maintain patterns long after they stop serving you.
✓ Peripheral vision activates the parasympathetic nervous system, creating conditions for alpha brainwave states.
✓ Catching the lie requires compassionate awareness, not willpower or shame.
✓ The Alpha Sequence provides a structured method for accessing the brain's teachable state.
✓ Change is possible when you guide your brain's creative capacity rather than fighting against it.
Your brain is lying to you, but only because it doesn't know how to upgrade itself without your help.
That's the beautiful part. You have conscious intervention available to you. You can teach it new shortcuts - ones that actually lead to real relief (rather than just leaning into the memory of a previous temporary feeling of relief).
The same creative capacity that makes lights seem to move on a still night can make peace, calm, and clarity feel real again. Your brain isn't lying to you out of malice or some built-in flaw. It's showing you how flexible perception really is, how much of your experience is constructed rather than fixed.
And that flexibility, that malleability of perception, is what makes transformation possible.
References
1 "How To Use Peripheral Vision In Therapy," NLP Pod, December 4, 2019. Foveal vision is linked to sympathetic nervous system arousal (activity, adrenalin, stress) while peripheral vision is linked to parasympathetic arousal (relaxation, calmness, healing). The two states are physiologically incompatible.
2 Fehmi, L., & Robbins, J. (2007). The Open-Focus Brain: Harnessing the Power of Attention to Heal Mind and Body. When clients imagined space (spacious awareness similar to peripheral vision), phase synchronous alpha brainwaves appeared in EEG readings—the same patterns found in elite athletes during flow states.
3 Nedelescu, H., et al. (2025). "Recruitment of Neuronal Populations in the Paraventricular Thalamus of Alcohol Seeking Rats with Withdrawal-related Learning Experience." Scripps Research, October 6, 2025. The study reveals that the PVT becomes hyperactive when animals learn that alcohol eases withdrawal symptoms, creating a circuit that drives relapse by linking substance use to relief from negative emotional states.
4 Multiple studies have demonstrated the PVT's role as a critical circuit node in addiction-related behaviors across the reward/acquisition, withdrawal, and relapse stages. See: Hartmann & Pleil (2021), "Circuit and neuropeptide mechanisms of the paraventricular thalamus across stages of alcohol and drug use," Neuropharmacology; Zhao et al. (2024), "Paraventricular thalamus to nucleus accumbens circuit activation decreases long-term relapse of alcohol-seeking behaviour in male mice," Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior.
5"TMJ & Vagus Nerve Connection: Relief & Regulation," Steph Edwards, August 14, 2025. The TMJ is closely linked to the trigeminal nerve, which connects to the vagus nerve in the brain. When jaw tension is released, it can help regulate vagal tone and activate the parasympathetic nervous system.
6"Vagus Nerve Yoga for Balance," Dr. Arielle Schwartz, December 30, 2024. Research has found that slow, rhythmic, diaphragmatic breathing with extended exhalation increases healthy vagal tone and activates the parasympathetic nervous system.

About The Alpha Sequence

The Alpha Sequence is a research-backed hypnotic technique designed to help you achieve nervous system regulation, clarity of thinking, and the ability to remain "in flow" for extended periods. By practicing for as little as 5 minutes per day, you can experience better sleep, improved motivation, and increased frequency of peak experiences.
Learn more: The Alpha Sequence Training